Report on European Analytical Capabilities for Hydrogen Purity According to ISO 14687 and Quality Assurance
This report is part of the HYDRAITE project, which seeks to strengthen the European hydrogen industry's capacity to meet rigorous fuel purity standards. As hydrogen is poised to become a key component in Europe's transition to cleaner energy, particularly in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), this report outlines the advancements made in developing independent laboratories capable of ensuring hydrogen fuel quality.
Table 1 provides the maximum permissible levels for total sulfur compounds in hydrogen, as defined by ISO 14687 and EN 17124.
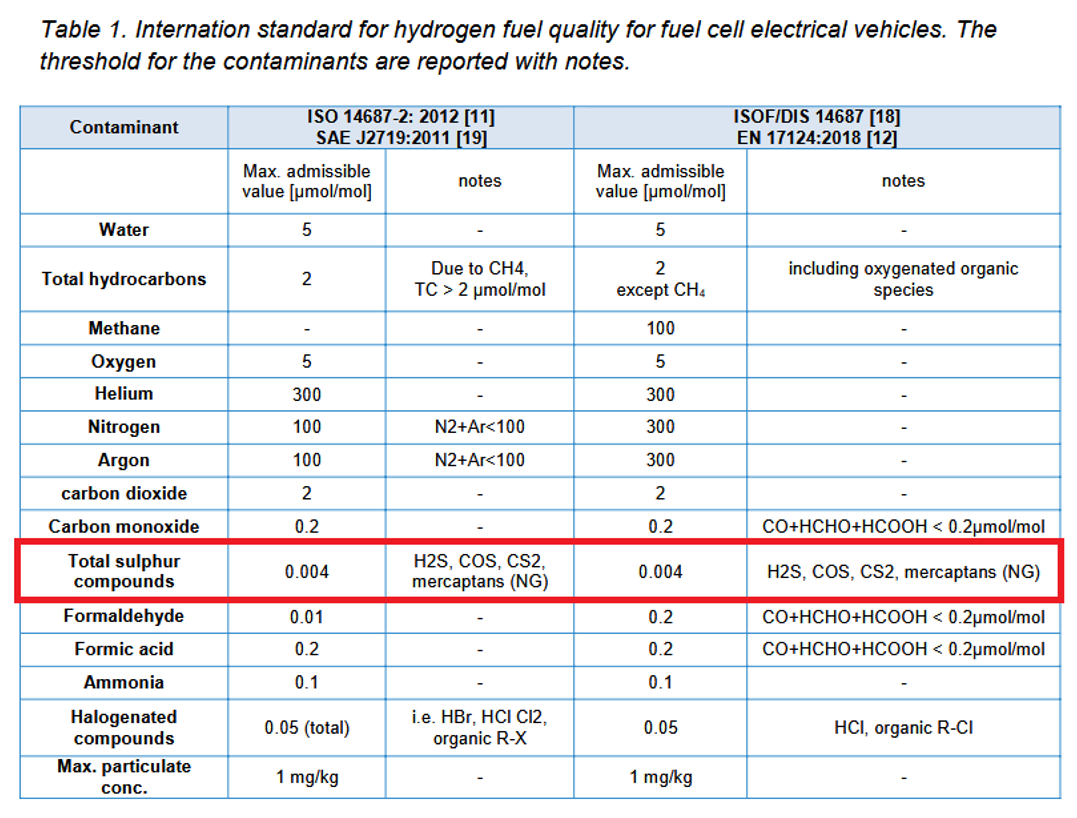
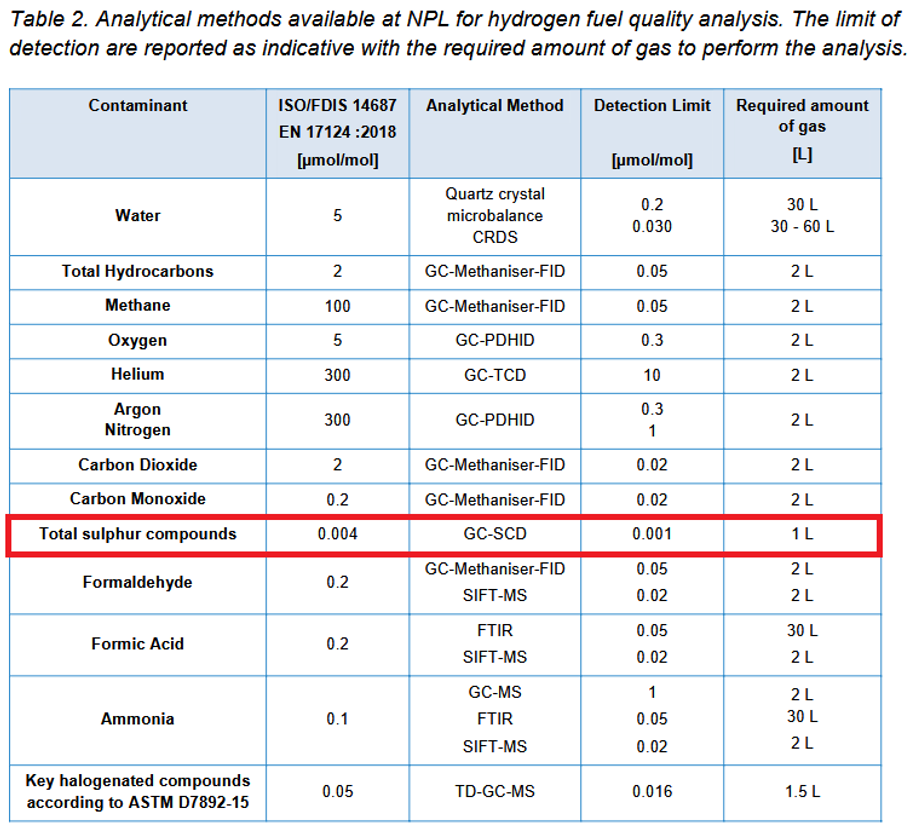
Table 2 further elaborates on the methods used by the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) to measure these sulfur compounds, detailing the sensitivity and precision of their analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography with sulfur chemiluminescence detection (GC-SCD). These tables highlight the importance of accurately monitoring sulfur levels to maintain hydrogen purity standards and ensure the reliable operation of FCEVs. Together, they reflect the vital role of sulfur analysis in advancing hydrogen fuel quality assurance across Europe.
 See Full Report
See Full Report
Saturation Testing Results of the SULFUR MAGNET FINAL FILTER®
The saturation testing of the SULFUR MAGNET FINAL FILTER® from Standard H2, Inc. demonstrated exceptional sulfur removal efficiency. The 6-inch filter, initially weighing 216.58 grams with 16.95 grams of Sulfur Magnet media, was exposed to hydrogen sulfide concentrations of 2000-5000 ppm in nitrogen at a controlled flow rate. After testing, the filter’s weight increased by 4.70 grams, indicating the removal of 9.40 grams of sulfur while releasing 4.70 grams of oxygen in the reaction converting H₂S to H₂O. This resulted in a saturation capacity of 55.4%, significantly higher than other known sulfur removal media. The testing process included initial and post-exposure purging with dry nitrogen for 12-16 hours each and was conducted at room temperature.
See Full ReportH2S Removal Report
Initial testing of the supplied filter/scrubber unit showed excellent performance in removing hydrogen sulfide. The analytical method was refined to achieve a detection limit of approximately 0.2 ppb (200 ppt). During testing, the filter was exposed to a constant flow of 1.902 ppm hydrogen sulfide in nitrogen after being purged with dry nitrogen for 12-16 hours. The filter reduced hydrogen sulfide levels to below detectable limits, achieving a gas purity of >99.99999998% (9N8 purity or better) under the tested conditions.
See Full ReportNOx Removal Report
Testing of the "FINAL FILTER" filled with the "SULFUR MAGNET" from Standard H2, Inc. demonstrated highly effective removal of nitrogen oxides. The analytical method was refined to achieve a detection limit of approximately 0.2 ppb (200 ppt). During testing, the filter was exposed to a constant flow of 2000 ppm nitric oxide in nitrogen after being purged with dry nitrogen for 12-16 hours. The filter reduced total nitrogen oxide (NOx) levels to below detectable limits, achieving a gas purity of >99.9999999% (9N purity or better) at a flow rate of 30 ml/min. Saturation levels and removal efficiency versus flow rates will be evaluated in subsequent studies.
See Full Report